Arching, upright shrub to 2 m (6 ft) tall. Bark red-brown and exfoliating. Twigs glabrous to sparsely pubescent; scattered to dense bristles. Leaves alternate, palmately compound, 3-5 foliate; leaflets ovate to ovate-lanceolate, 5-15 cm (2-6 in) long; sparsely pubescent above, gray-woolly beneath; dark green above, pale below; rounded to cuneate at base; acuminate at apex; margins serrate or doubly serrate; stipules linear, tapering toward apex. Inflorescence a leafy raceme of 1-4 flowers; calyx 5-lobed, without glands or stipitate-glandular, reflexed; petals 5, white, erect; styles pistils many, inserted on hypanthium; stamens numerous; flowers appear from May to July. Fruit an aggregation of drupelets, 12-18 mm (0.5-0.75 in) in diameter, oblong, red-black; fruits mature July to September.
Distribution: Broadly distributed throughout North America.
Habitat: open woodland and streamsides.
Comments: Rubus is a Roman name meaning red; idaeus means of Mount Ida.
Field identification: Rubus is a complex genus. Species are difficult to identify due to frequent hybridization and introgression.
Medicinal uses: The Chippewas used the inner bark of the root to treat cataracts.
Food uses: the fruits are large and tasty. They can be eaten raw or used in jams, jellies, and sauces.
Wildlife benefits: raspberry fruits are eaten by many species of birds and mammals.
NWI status: UPL, FAC.
Distribution in Oklahoma: 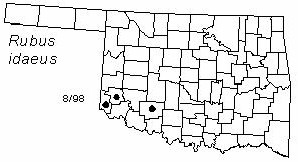
BACK
NEXT
RETURN TO INDEX
Last update: 9/17/99
 Go to Oklahoma Biological Survey Home Page
Go to Oklahoma Biological Survey Home Page
 Disclaimer
Disclaimer